Plant-atmosphere interactions
The Final Exam
The final exam will be open between April Wednesday April 24th and Thursday April 25th. It will be completed asynchronously over canvas.
- The exam will not be timed. It is not intended to take longer that a normal exam period (250 minutes), but I want you to have more time if you need it.
- The exam will be open for 48 hours starting at 8 AM Wednesday April 24th
- Late submissions will not be accepted. If you experience extenuating circumstances, contact me before the exam period closes
- The exam will be open for 48 hours starting at 8 AM Wednesday April 24th
- The final is cumulative; any topics from the course are fair game. Similar to the midterm:
- A collection of multiple choice, fill in the blanks, matching etc. (~50%)
- Problem set + short answer questions (~50%)
Teaching Evaluations (iClicker)
Have you filled out an evaluation yet?
- A Yes
- B No, but I will
- C No, and I don’t plan to
About Evaluations
- They are completely anonymous!
- They matter!
- I read every comment & value constructive feedback!
- This was my first time teaching the course, so I would like to know how I could improve it!
- You can follow this link to the evaluation
Learning objectives
- Explain why plant processes are important for the atmosphere.
- Assess the importance of the energy absorbed in photosynthesis or heat released by respiration.
- Describe what controls the exchange of water and carbon between a leaf and the atmosphere.

Photosynthesis across the globe
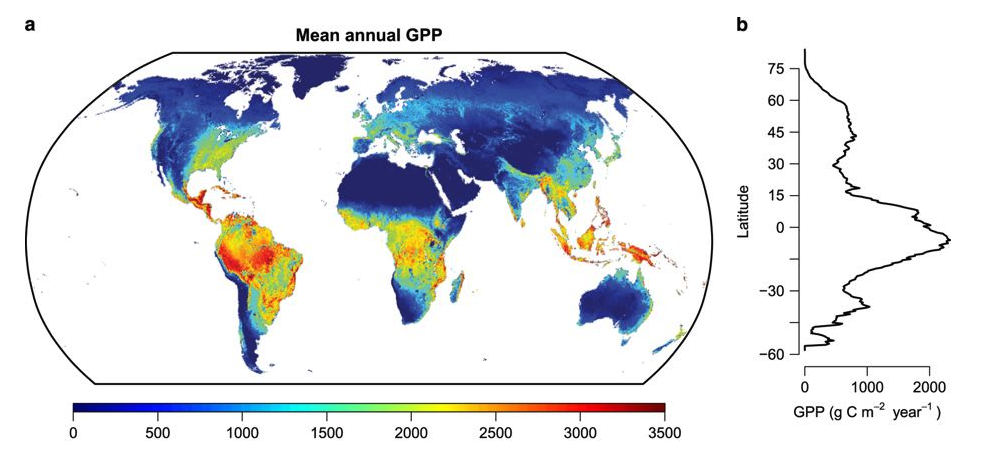
The land sink for CO2
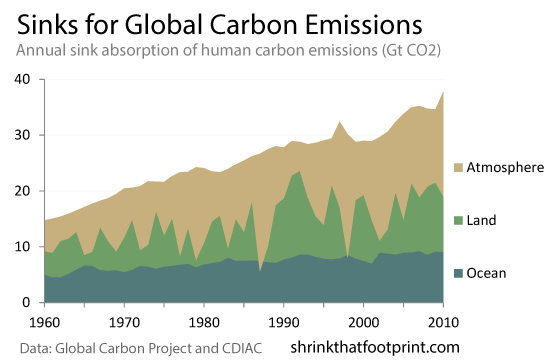
Looking Inside a Leaf
Plant-Atmosphere Exchnage
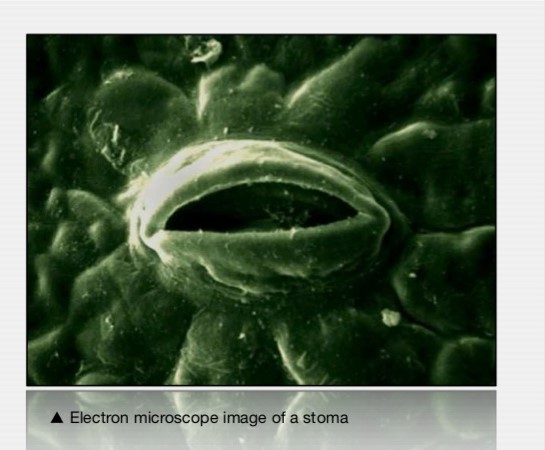
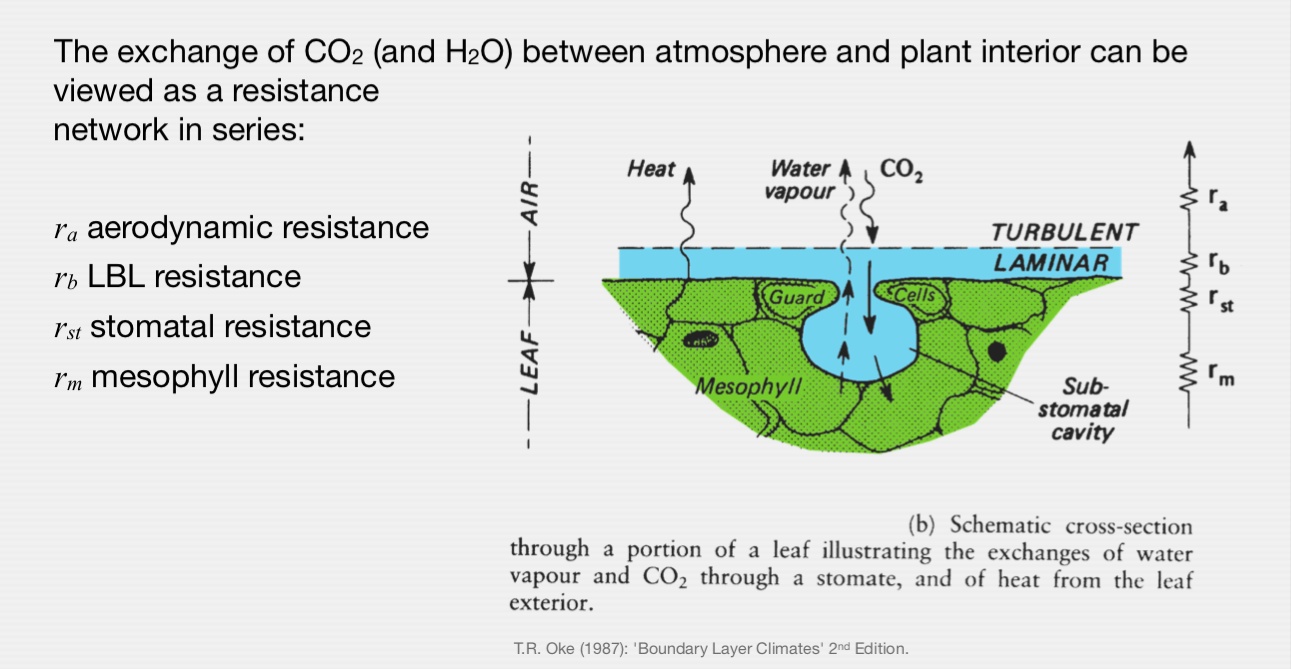
Exchange of CO2, H2O, and O2 between plant interior and atmosphere occurs through stomata.
- Found on the underside of the leaf
- Open/close to regulate exchange
Photosynthesis vs. Respiration

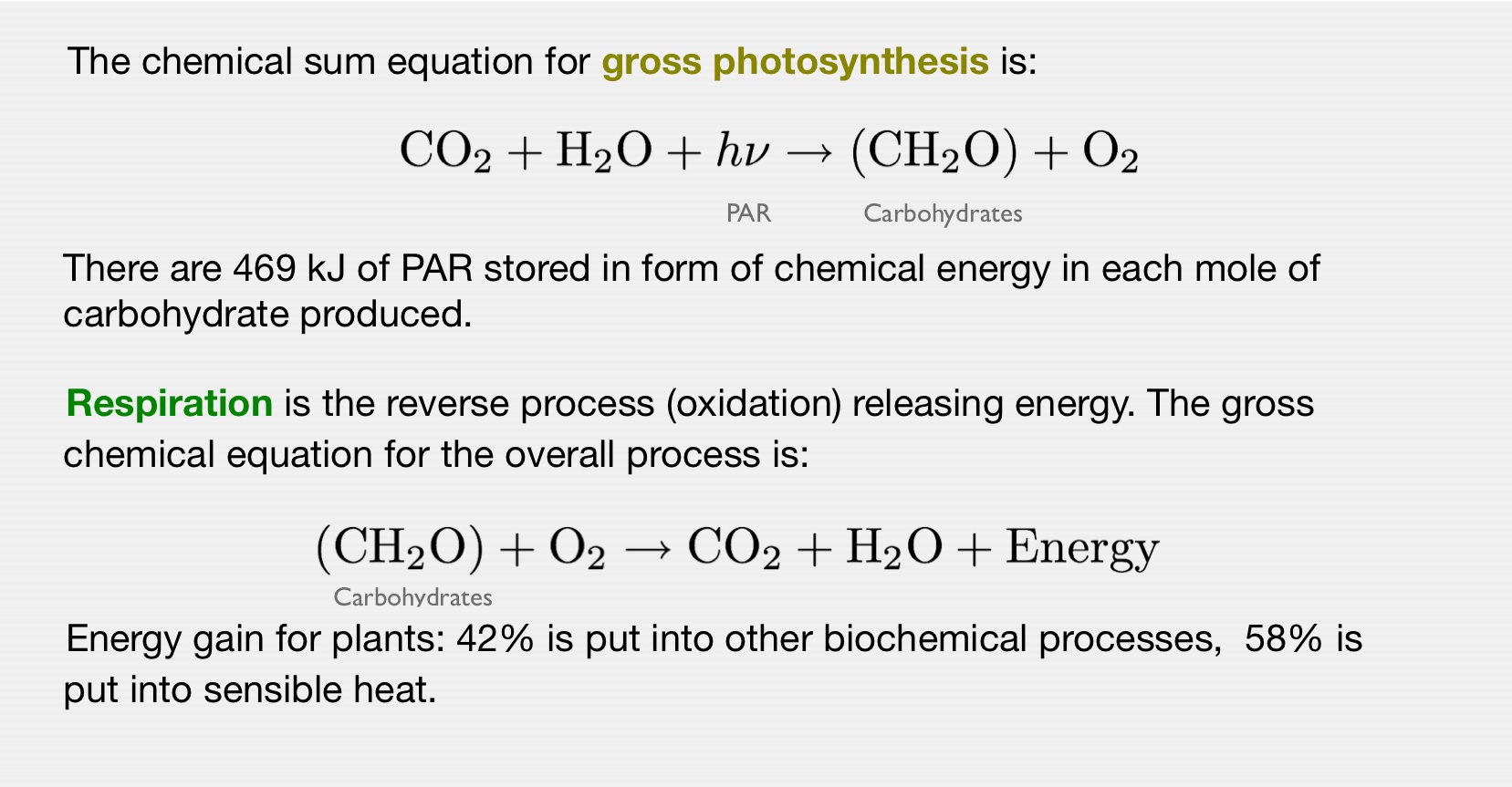
Gross chemical processes
Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE)
Defined by atmospheric scientists; the atmosphere is the reference reserviour for CO2; Units are generally in mol m-2 s-1 or g m-2 s-1. Negative values indicates uptake by the ecosystem, positive indicates accumulation in the atmosphere:
\[ NEE = F_c = \overline{w^{\prime}\rho_c^{\prime}} \]
Net ecosystem productivity (NEP)
Reference reserviour for CO2 is the ecosystem. In simple cases, \(NEP \approx - NEE\). NEP is more comprehensive; it also includes land-water fluxes, but much more difficult to measure.
It is defined as the difference between ecosystem Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) and Ecosystem Respiration (ER) :
\[ NEP = GPP-ER \]
ER is the total aerobic respiration of CO2 by an ecosystem:
\[ ER = AR + HR \]
- Autotrophic respiration (AR) is CO2 respired by primary producers (plants)
- Heterotrophic respiration (HR) is CO2 respired by all other living organisms (bacteria, animals, fungi). This CO2 is also derived from GPP, but in a more roundabout way.
Carbon uptake or release from ecosystems?
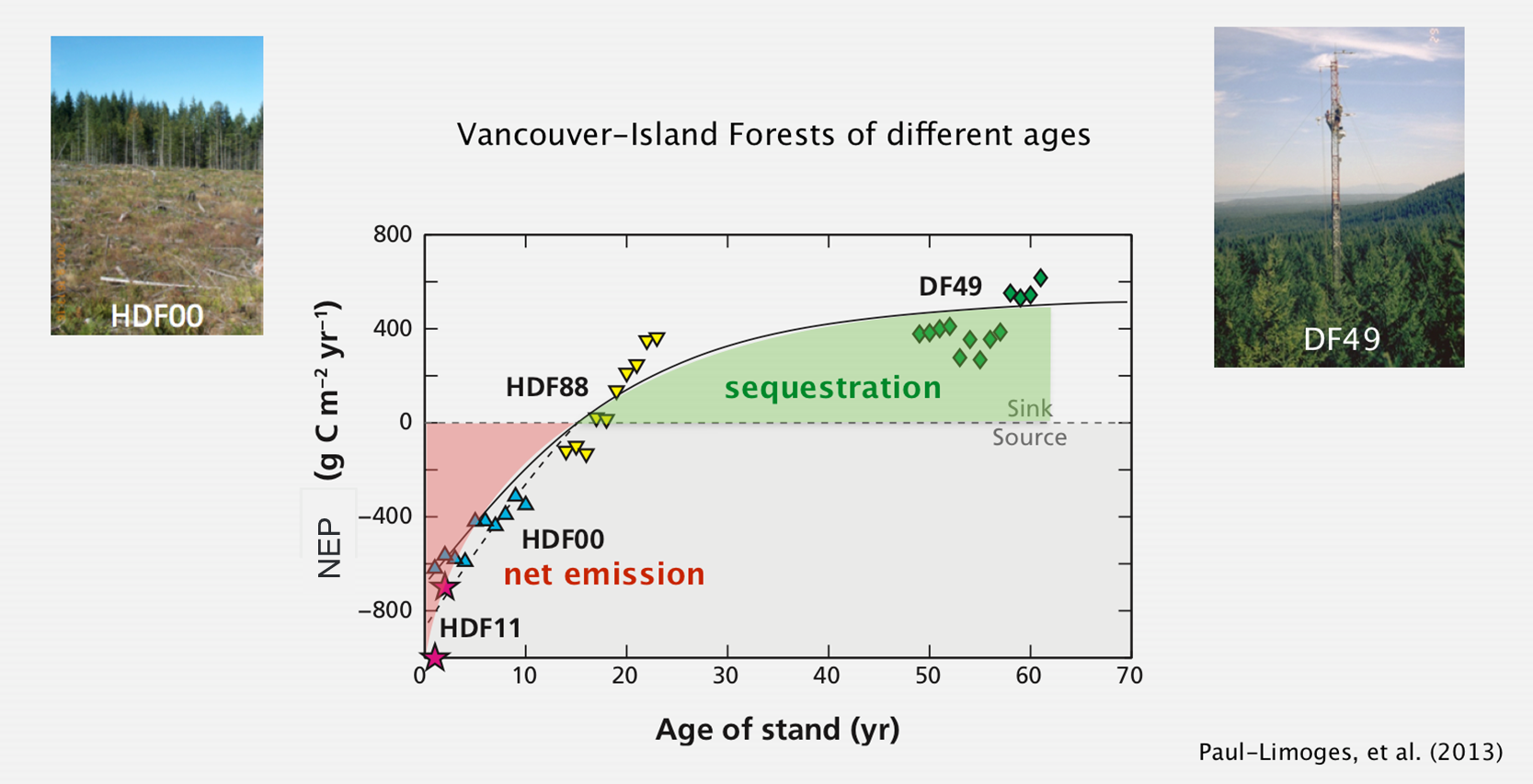
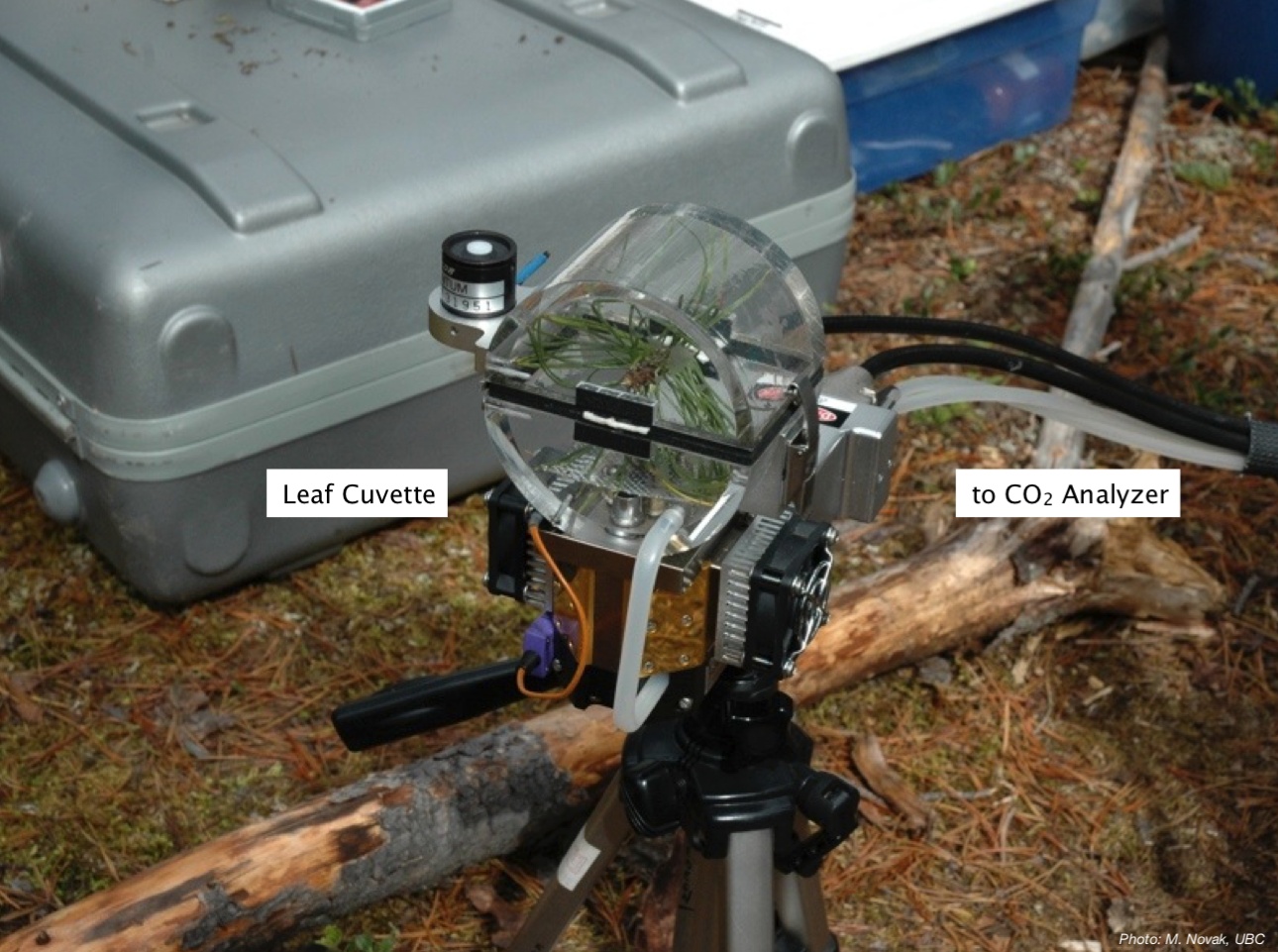
Energy Balance & NEP
Energy absorbed in photosynthesis or heat released by respiration can be expressed as a storage term in W m-2:
\[ \Delta P = \Phi NEP \]
where \(\Phi\) is the heat of assimilation of carbon, which is 469 kJ mol-1, or aproximately 3 W h g(CO2)-1.
\(\Delta P\) is small; often neglected in energy balance calculations
- Stomatal control of transpiration is much more relevant in the surface energy balance!
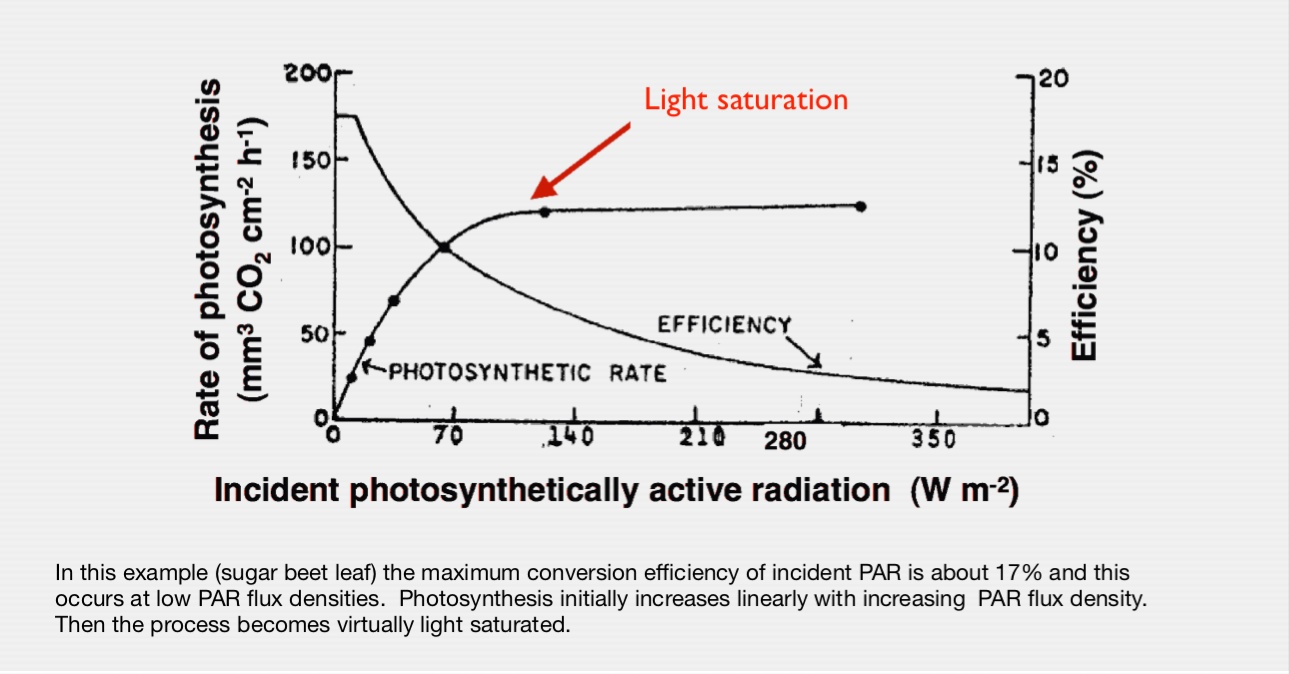
Conversion Efficiency
PAR (0.4 to 0.7 \(\mu m\)) is ~ 50% of \(SW\)
- Effieciency of PAR absoprtion is < 20%
- Since > 50% of this goes to heat; < 10% of energy from \(SW\downarrow\) is converted to chemical energy
- 10% is an upper limit under optimal conditoins
- In reality it is often < 1%
- Water & temperature stress, sub-optimal light intensities, nutrient limitations, etc.
- In reality it is often < 1%

Light response curve & light saturation
Exchange of water through plants
When stomata are open:
- They expose the moist plant interior to dry ambient air
- As they take up CO2, they loose H2O
- This is transpiration
Evaporation vs. transpiration

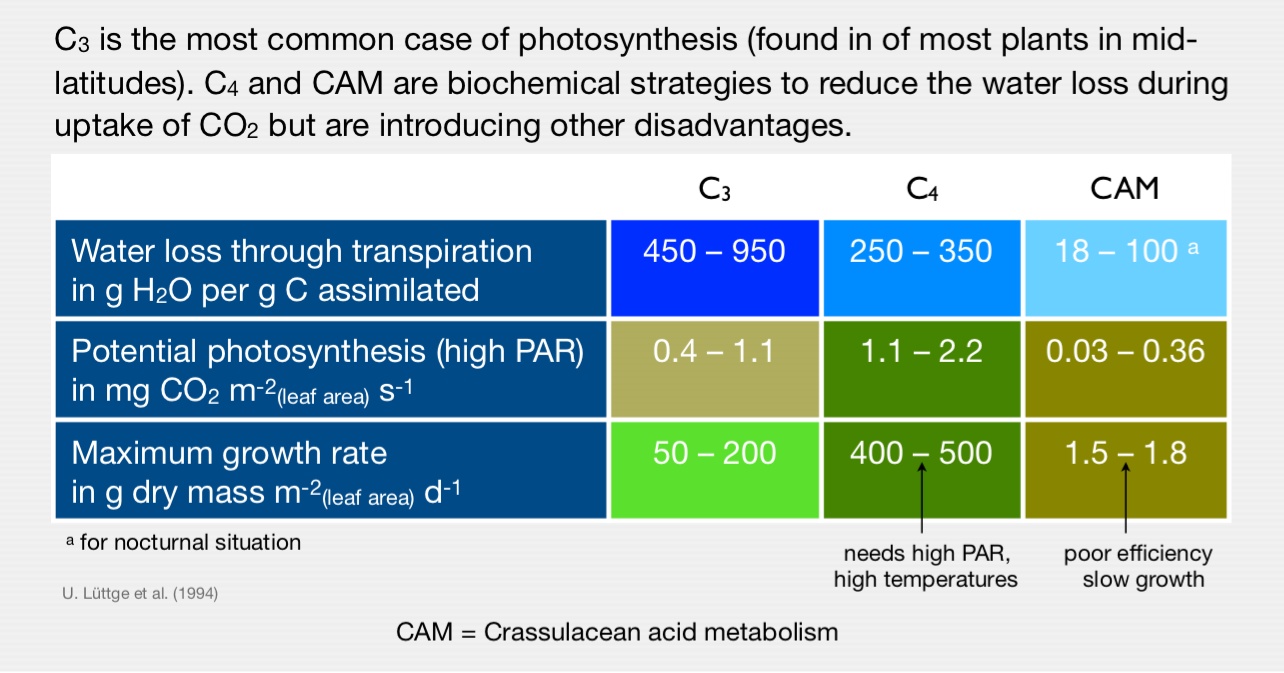
Photosynthesis – Biochemistry Rules Efficiency
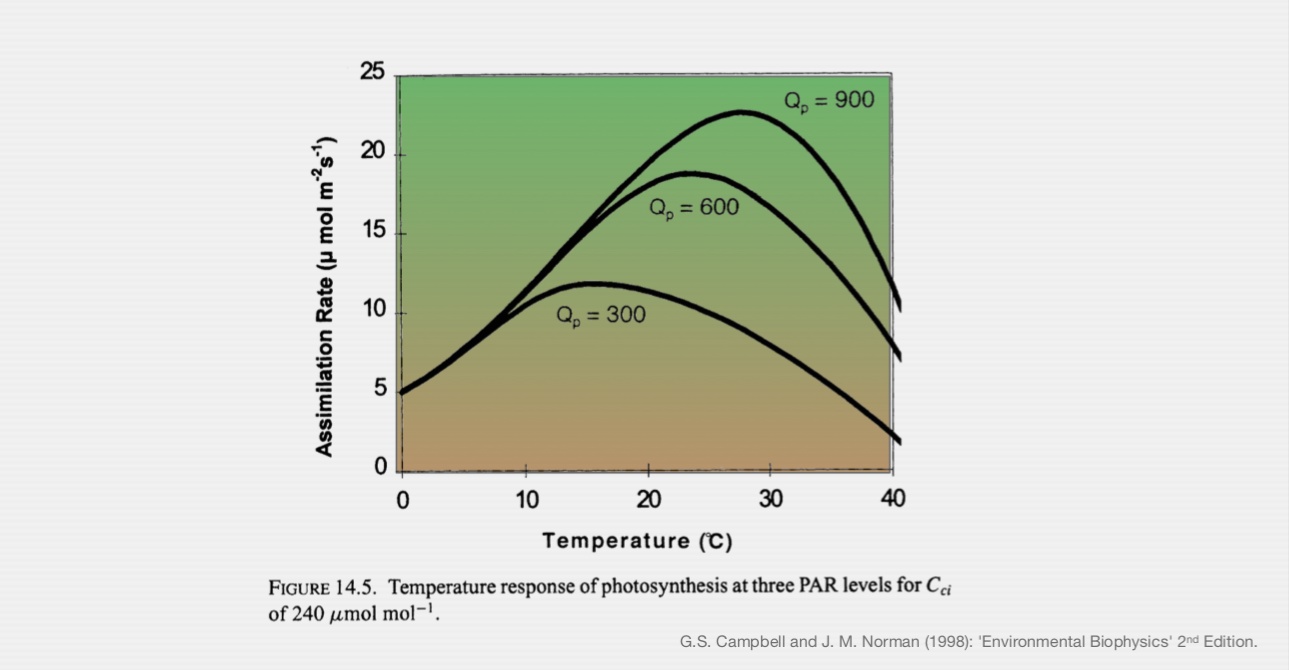
Temperature Response of Photosynthesis
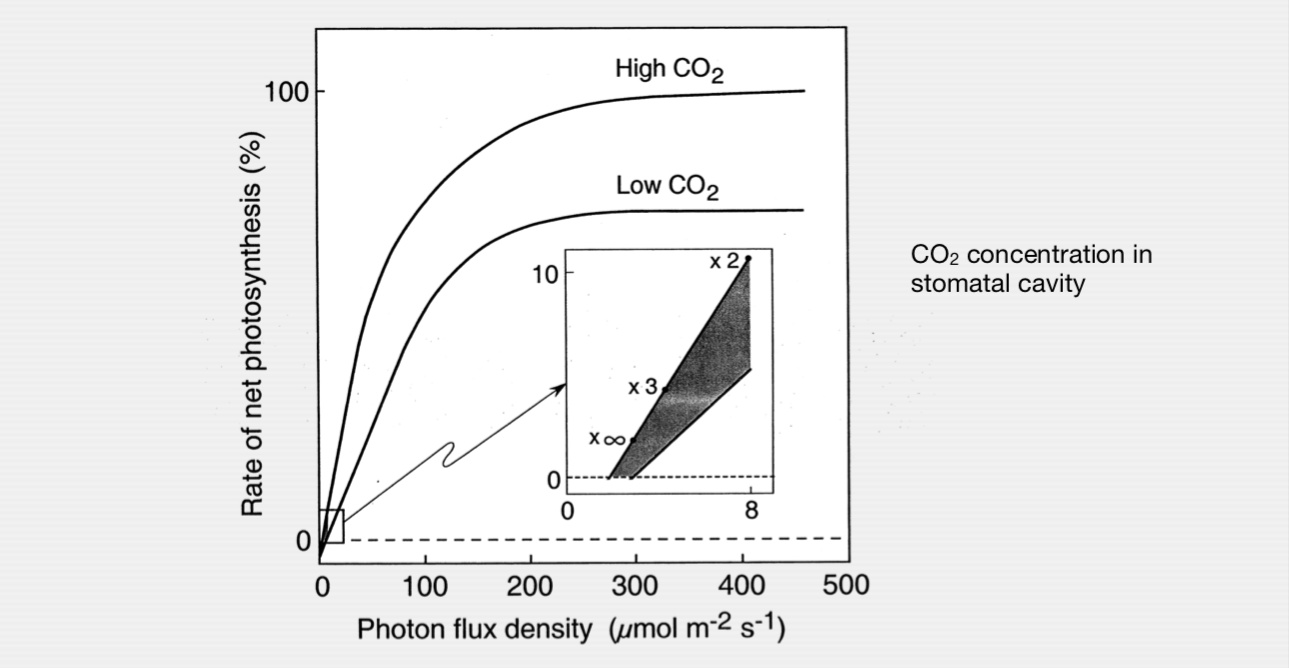
CO2 Response of Photosynthesis
Resistance Approach
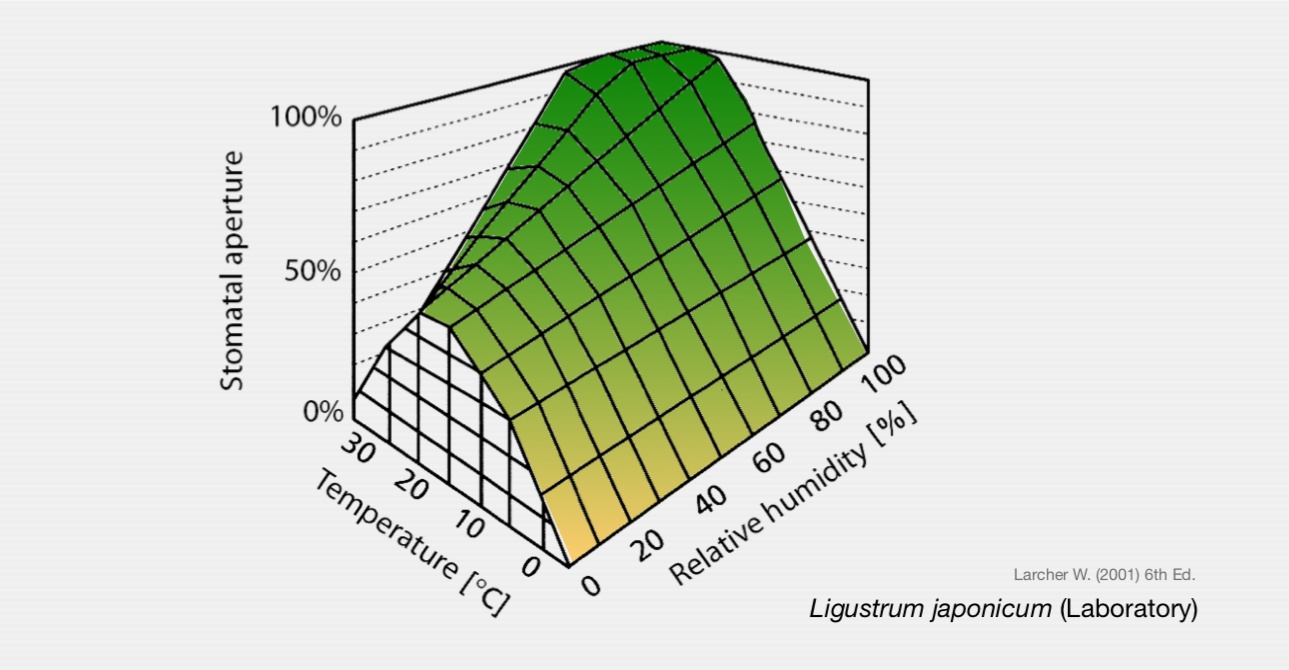
Stomatal Response to Humidity and Temperature
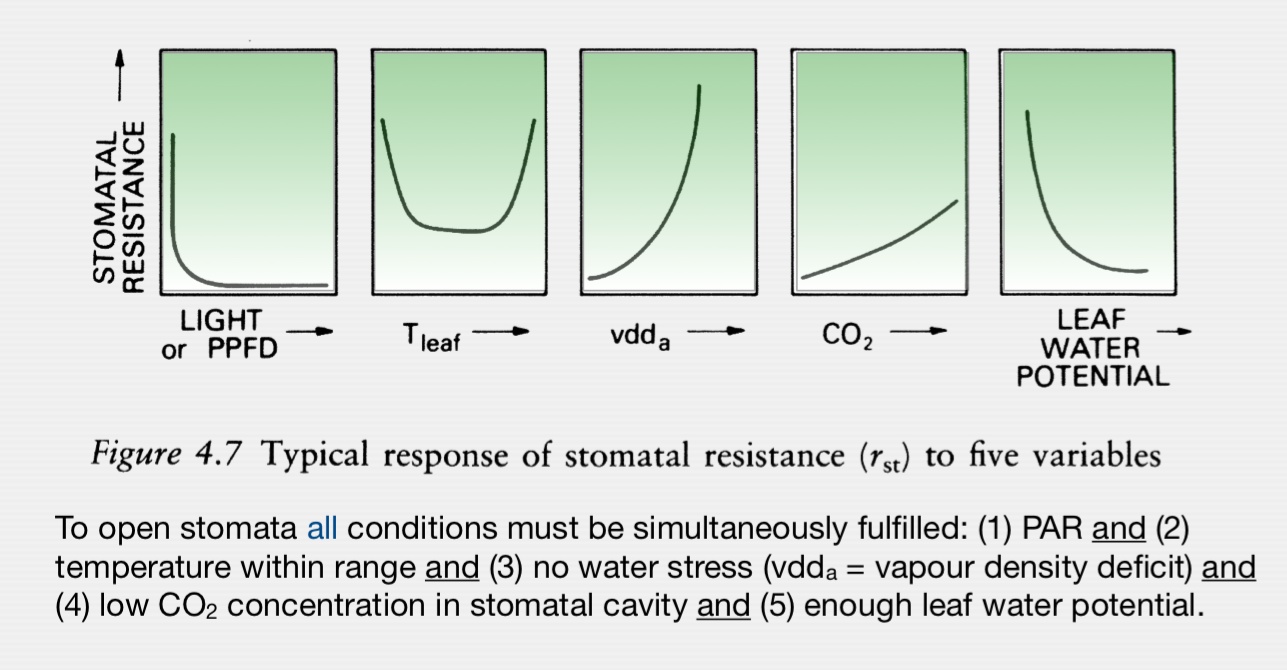
Stomatal Resistance
Timelapse: photosynthesis from space
Take home points
Ecosystems take up CO2 by photosynthesis and release it by respiration.
Energy used by photosynthesis is minor, won’t exceed 10% of \(R_n\)
Stomatal resistance is a very important control over partitioning of \(LE\) and \(H\)
Properly representing stomatal resistance is essential for weather and climate models.